Generative AI has evolved from a lab experiment into a must-have coding companion. Fueled by transformer-based language models trained on billions of lines of source code and natural language, these systems can spin a single prompt into anything from a concise snippet to a production-ready application.
By offloading boilerplate, documentation, and test generation, they free engineers to focus on the real business problems that move a product forward.
So which assistants are worth your time? Below is a quick tour of 13 standout generative-AI coding tools, what they do best, where they fit, and why they’re gaining
1. GitHub Copilot

GitHub Copilot is perhaps the best-known AI coding assistant among developers. Powered today by the GPT-4.1 Copilot model for inline completions with optional GPT-5-preview “Smart mode” in Copilot Chat, it behaves like an always-on pair programmer across VS Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDEs, Neovim, and the browser.
Key features
- Natural-language & chat prompts: e.g., “sort a list of integers” or “generate Jest tests for this module”.
- Multi-model routing: Pick fast o-mini, balanced GPT-4.1, or deeper-reasoning GPT-5 for each query.
- Wide IDE coverage: Official extensions for VS Code/Visual Studio, JetBrains, Neovim, GitHub Mobile, plus a browser playground.
- Context awareness: Leverages nearby files, project dependency graphs, and Git history for more relevant completions.
- Governance controls: Enterprise tenants can disable context upload, set retention policies, and filter output against non-permissive licences.
2. Amazon Q Developer (formerly CodeWhisperer)

Amazon Q Developer is AWS’s next-generation generative AI coding assistant. It replaces CodeWhisperer, preserving all legacy capabilities while introducing new agent-driven workflows. Available in VS Code, JetBrains IDEs, Visual Studio, Eclipse, and the CLI, it offers context-aware completions, conversational help, and supports agent-driven workflows such as refactoring, testing, and PR creation.
Key features
- AWS integration: Suggests the right SDK calls, IAM policies, CloudFormation/CDK templates, and service configurations
- Security scanning: Continuously (or on demand) flags vulnerabilities and proposes fixes
- Reference tracking: Warns when a completion resembles public-source code and links the licence & repo URL
- Agentic workflow: Slash commands like /dev, /test, or /transform plan multi-file edits, run shell commands, and raise PRs
3. Tabnine

Tabnine positions itself as the “AI you control.” Its Universal and Protected models are trained exclusively on code with permissive licences (MIT, Apache-2.0, BSD, etc.), eliminating most copyleft risk. For enterprises that need deeper relevance, Tabnine can fine-tune a private model on your own repositories, all inside your VPC or air-gapped network.
Key features
- Custom models: Organizations can train Tabnine on their private repositories, producing context‑aware suggestions.
- Deploy anywhere: Cloud SaaS, private VPC, on-prem, or fully air-gapped (only for enterprise customers), all with end-to-end encryption and zero data retention.
- Multi‑language support: Tabnine works with popular languages such as Python, Java, C++, Go, and more.
4. Replit AI

Replit AI is the inline assistant integrated into Replit’s cloud IDE. It watches every keystroke, offers context-aware completions, rewrites code on command, and drafts docstrings or README sections without leaving the browser.
Key features
- Docstring & README generation: Auto-summarizes functions or inserts project docs as you code.
- In-browser run & debug: Start servers, set break-points, inspect logs, and view live previews without installing anything locally.
- Agent 3 autonomy: Up to 200 minutes of continuous work on Pro plans; free tiers have shorter execution windows.
5. Code Llama (Meta)
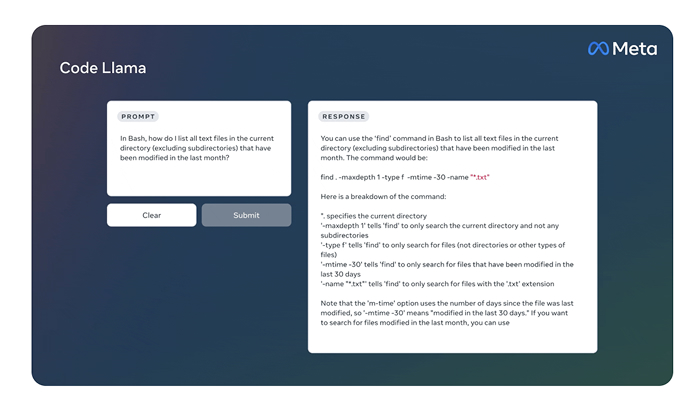
Code Llama is Meta’s LLM built on Llama 2 and specialized for programming. Fine-tuned on billions of lines of source code and natural language, it can write functions, explain snippets, or fill in the middle of an existing file. It supports popular programming languages such as Python, C/C++, Java, TypeScript, C#, PHP, and Bash.
Key features
- Fill-in-the-middle (FIM): Insert the model between existing code blocks; it infers missing logic and preserves style.
- Multi-size, multi-variant family: 7B, 13B, 34B, and 70B checkpoints, each with Base, Python, and Instruct flavours; 16K-token context window. The 70B model is most commonly used via fine-tuned Instruct variants.
- Open weights & licence: Download, run, or fine-tune in your own environment; permissive for commercial use (few restrictions vs. copyleft).
6. CodeT5/CodeT5 +
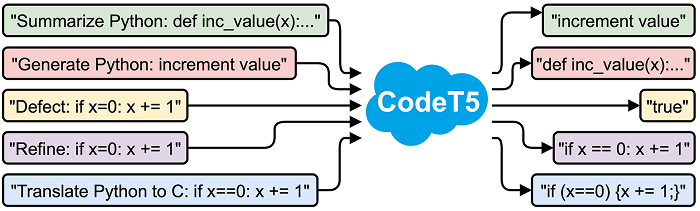
CodeT5 (2021) and its scaled successor CodeT5 + (up to 16B parameters) adapt Google’s T5 architecture to source code. The BSD-3-Clause licence lets companies download, fine-tune, and deploy the models without licensing fees, making CodeT5 one of the most flexible, self-hostable options on the market.
Key features
- Natural-language programming: Generate complete functions or file scaffolds from descriptive prompts across Python, Java, Go, C/C++, TypeScript, C#, PHP, and more.
- Bidirectional seq2seq architecture: The encoder-decoder design supports both generation (decoder) and understanding tasks, such as summarization or defect detection (encoder).
- Open weights & fine-tuning: CodeT5+ offers models up to 16B parameters (with smaller variants around 220M, 770M, and 2B).
7. Durable AI

Durable AI isn’t a coding assistant in the strict sense. It’s a no-code AI website builder. Provide a few basic details about your company, and within 30 seconds, Durable creates a multi-page, mobile-friendly website with copy, stock imagery, and SEO metadata.
Key features
- Context-driven autocomplete & chat: Suggestions respect your naming conventions, test helpers, and internal libraries.
- AI copy, images & SEO: Auto-writes marketing copy, selects industry-appropriate visuals, and applies basic on-page SEO so the site is ready for search engines out of the gate.
- Built-in business tools: Optional CRM, invoicing, blogging, and email-marketing modules extend the site into a lightweight growth platform.
8. Cody by Sourcegraph

Cody is Sourcegraph’s AI assistant that uses context from your code base to provide tailored suggestions. It offers auto-completion from a single line to entire functions and supports multiple languages. Cody integrates with Sourcegraph search, enabling you to locate definitions, references, and documentation while writing.
Key features
- Deep context awareness: Before answering, Cody searches your repos for relevant files, symbols, and docs.
- Multi-model choice: Pick GPT-5, GPT-4o, Claude 4, Gemini 2.5, or OpenAI 4.1 mini/ nano; routing happens through Cody Gateway.
- IDE & web support: Official extensions for VS Code, JetBrains, Visual Studio, and a browser IDE; same chat UI everywhere.
- Clarification: Cody doesn’t host its own models. It routes to external LLM providers (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic, Google) through the Cody Gateway for completions and chat responses.
9. Cursor AI

Cursor is a VS Code-compatible editor rebuilt around AI. You still get the familiar key-bindings and extensions, but every pane is super-charged by large-language-model helpers from 200k-token autocomplete to autonomous agents that refactor code while you grab coffee.
Key features
- Inline & multi-line completions: Suggests entire blocks, unit-tests, or config files; accepts with TAB.
- Auto-edit & Smart-Apply: Highlight code → “make async” → Cursor rewrites and opens a diff.
- Agent Mode & Background Agents: Plan multi-step tasks, edit many files, run shell commands, test, and retry.
- Model gateway & context control: Flip between GPT-4o, Claude 4, Gemini 2.5, or local Llama; Normal mode gives 128k tokens. Max Mode defaults to ~200k and can scale up to ~1M tokens for enterprise plans.
10. Gemini

Gemini is Google’s flagship large-language-model family (successor to Bard) and now ships in three developer-friendly forms:
- Gemini Apps (web/chat): quick prompts, code explanations, Colab export.
- Gemini Code Assist: an IDE plug-in for VS Code and JetBrains that offers completions, refactors, and chat-based Q&A powered by the Gemini 2.5 model, currently in public preview.
- Gemini CLI: a command-line agent that answers natural-language prompts inside your terminal and can hand off tasks to Code Assist.
Key features
- Multi-language support: Generates, explains, and debugs code in 20+ languages (Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Go, Java, TypeScript, Sheets formulas, etc.).
- Export to Colab and Google Sheets: One-click export of Python snippets to Google Colab; auto-writes =ARRAYFORMULA() and other Sheets functions.
- IDE integration (Code Assist): Inline completions, chat-refactor, “smart actions,” and Firebase-aware snippets in VS Code/IntelliJ.
11. StarCoder

StarCoder (2023) and its successor StarCoder 2 (Feb 2024) are fully open-access code-generation models stewarded by the BigCode collaboration (ServiceNow Research, Hugging Face, NVIDIA).
They are trained on permissively licensed data from more than 80 programming languages and 1 trillion tokens. StarCoder can autocomplete, modify, and explain code, and it supports an 8k+ token context window.
Key features
- Fill-in-the-middle & long-context reasoning: Drop the model between existing code blocks; it infers missing logic while retaining surrounding style.
- Polyglot coverage (600+ languages): Solid performance from Python and C++ to niche DSLs.
- Self-host or fine-tune: Weights on Hugging Face let you run StarCoder on-prem, quantize for GPUs/CPUs, or fine-tune with PEFT/LoRA.
12. ChatGPT

OpenAI’s ChatGPT is a general-purpose LLM that can assist with programming. The public chat product now defaults to GPT-4o (or even GPT-5 for Plus/Pro users) and ships with an integrated Code Interpreter sandbox that can run Python, read uploaded files, and return downloadable results, all inside the chat window.
Key features
- Conversational interface: Explain snippets, draft boilerplate, generate tests, or refactor functions in natural language.
- Third-party “apps” & SDK: Invoke partner services (e.g., Figma, Zillow) or build your own app that lives inside ChatGPT.
- Large context & multi-modal I/O: 128k-token window (GPT-4o), images & audio in/out.
- Python Code Interpreter: Runs code, analyzes data, converts files, and produces plots directly in chat.
13. Claude

Claude is Anthropic’s safety-first AI assistant. Its Sonnet 4.5 release (Sept 2025) has vaulted to the top of developer benchmarks, scoring 70.6% on SWE-bench Verified, the highest of any public model.
Built on Anthropic’s “constitutional AI” approach, Claude combines agent-grade reasoning with one of the largest context windows available, up to 1 million tokens, letting it ingest an entire codebase, trace dependencies, and propose multi-file fixes in a single request.
Key features
- 1M-token context: Analyse huge monorepos or lengthy design docs without chunking.
- Root-cause debugging & auto-patch: /fix and /security-review commands scan code, pinpoint bugs or vulnerabilities, generate patches, and open pull-requests.
- Benchmark-leading coding skill: Sonnet 4.5 tops SWE-bench Verified at 70.6%, outperforming GPT-4o and Gemini 2.5 on real-world repo issues.
- Safety & compliance: OpenRAIL-M licence, PII redaction, attribution tracing, and a public system card that details alignment safeguards.
FAQs
Q1. Can I generate production-quality code with generative AI?
Yes, if you treat the model as a junior teammate. Modern assistants can emit clean, idiomatic code, but they still hallucinate APIs, miss edge cases, or introduce security flaws. High-performing teams pair the AI with unit/integration tests, static analysis, SCA/license scans, and human review before merging.
Q2. Open-source vs proprietary tools: key trade-offs?
- Open-source models (e.g., Code Llama, StarCoder, CodeT5) offer transparent data, self-hosting, and full fine-tuning freedom, but you own the GPUs, patching, and support.
- Proprietary SaaS (Copilot, Gemini Code Assist, Claude, etc.) delivers turnkey IDE UX, cloud-scale context windows, and built-in vuln/ licence scanning at the cost of vendor lock-in, usage fees, and limited insight into training data.
Q3. How much human oversight is needed?
Keep the “junior-dev rule”: every AI change must pass automated tests and a senior-engineer code review. Most teams also gate on licence and security scanners before merging to main.
Q4. Best-suited tasks for generative AI tools?
- Boilerplate scaffolding (API handlers, test stubs)
- Refactoring and documentation generation
- Code translation between languages or frameworks
- Query/config generation (SQL, IaC)
- First-pass unit tests or edge-case suggestions
Conclusion
Generative-AI assistants are now tied into everyday development workflows, suggesting boilerplate, refactoring legacy code, generating tests, and even drafting pull-request diffs. Yet they remain helpers, not replacements. Their suggestions can miss edge-cases, leak sensitive data, or smuggle in license-incompatible snippets. Teams that see real productivity gains pair the models with:
- Automated guardrails: unit + integration tests, static-analysis, dependency and licence scanners
- Human oversight: senior code review and secure-by-design checklists
- Clear usage policies: what data the model may ingest, where its output may be stored, and how provenance is tracked
Used this way, generative-AI tools let developers spend less time on repetitive boilerplate and more time on architecture, performance, and product innovation, turning “write code” into “ship solutions” faster and more safely than before.