In today’s software projects, code changes happen at lightning speed—there are dozens of commits daily, automatic builds, and several environments on the go. With this speed comes a risk. A tiny typo, a rogue merge, or a sneaky library can slip through and alter the app’s behavior in production without a trace. To ensure every release is safe, teams must prove that the code they ship is the same code they reviewed and tested.
That proof is code integrity, also known as software integrity. When every binary, script, or container image is linked back to a signed and authorized build, the team can release with peace of mind, detect tampering immediately, and satisfy the security and compliance levels the business requires.
What is Code Integrity?
Code integrity means verifying that no one has tampered with, damaged, or swapped the code after it has passed QA. Simply put, the bits running in production must be the same bits that got the final approval.
This principle matters even more in distributed systems that depend on third-party libraries, CI/CD pipelines, and shared repos. A single bad commit or a forgotten configuration can trigger an immediate disaster.
Why Does Code Integrity Matter?
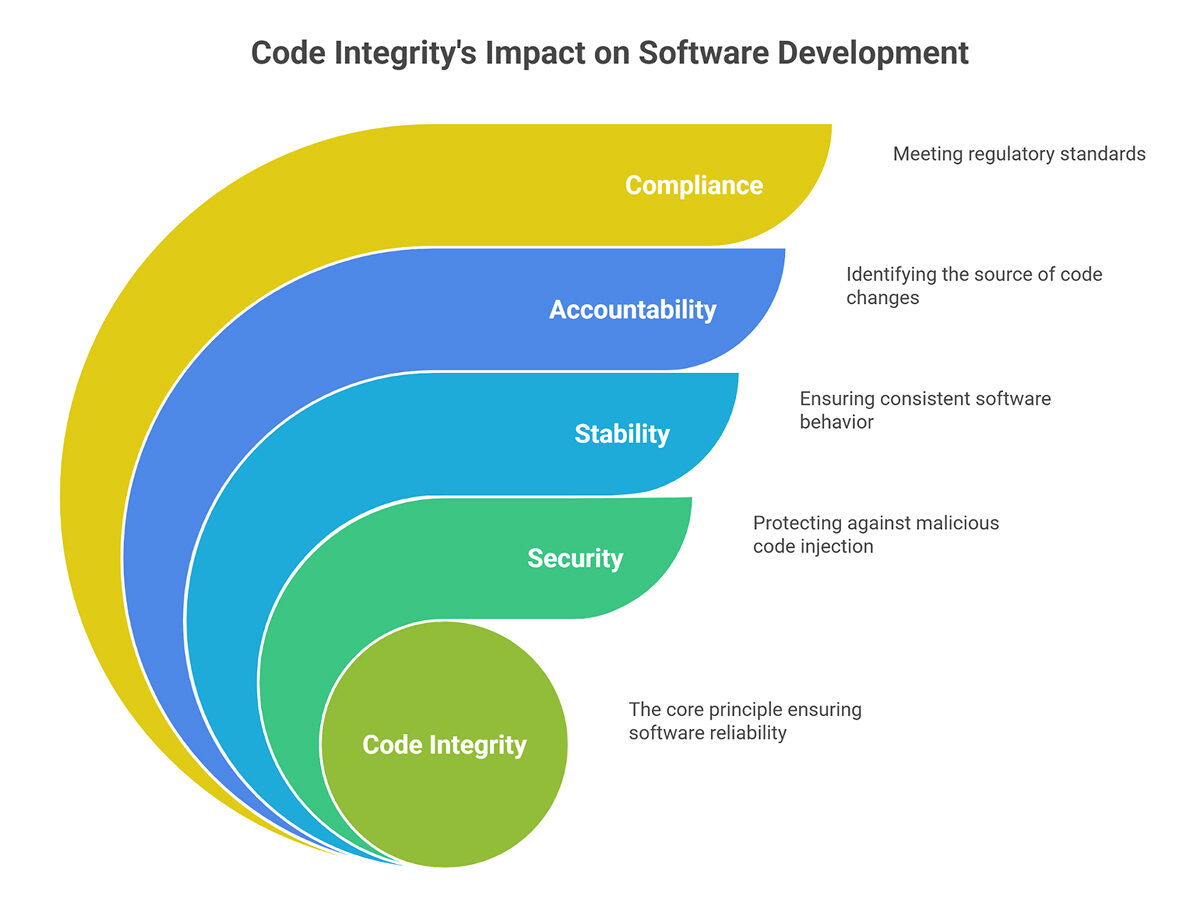
When an app misbehaves in production, code-integrity checks often lead investigators straight to the culprit.
- Security: Prevents bad or damaging programming from occurring.
- Stability: Guarantees the same behavior in development, staging, and production.
- Accountability: Traces every change and flags surprises.
- Compliance: Satisfies regulations such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and ISO/IEC 27001.
How Is Code Integrity Enforced?
Achieving software integrity isn’t a single magic button. It’s a layered approach of tools, policies, and good habits.
Code signing and digital fingerprints
- Developers hash or sign every build. At runtime, the system verifies that signature.
- Example: Windows now uses Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC), the successor to Device Guard, to block unsigned or untrusted executables.
Version control and commit traceability
- Git (or a similar tool) records each change so reviewers can catch unexpected edits.
CI/CD validation pipelines
- Automated tests and signature checks run before deployment, blocking tampered builds at the gate.
Runtime tamper detection
- Tools like Jscrambler inject anti-tamper code into JavaScript to detect in-browser modifications.
What Is a Code Integrity Policy?
A code integrity policy defines:
- What code is trusted
- Which checks are mandatory
- How violations are reported and handled
- Who is allowed to approve changes
Enterprises enforce policies with tools such as WDAC on Windows or Kubernetes admission controllers.
Code Integrity vs. Code Quality – Are They the Same?
No, they’re related but distinct.
- Code quality = readability, maintainability, and adherence to best practices.
- Code integrity = proof that the code hasn’t been altered after validation.
You can have perfect style but poor integrity (e.g., a hacker adds a payload). Conversely, strong integrity controls can protect a messy legacy codebase.
Common Challenges in Code Integrity
Awareness is the first step toward prevention. Here are the usual suspects:
- Malicious third-party libraries
- Compromised build environments
- Unauthorized commits or branches
- Supply chain attacks
- Manual changes in production
Best Practices for Maintaining Code Integrity
Let’s keep it practical. These are the habits and systems every team should embrace.
- Use code signing for scripts, DLLs, and executables
- Scan dependencies using tools like Snyk or OWASP Dependency-Check
- Lock dependencies via lockfiles (e.g., package-lock.json, Pipfile.lock)
- Enable audit trails on Git repositories (via GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
- Use CI/CD gates that block unauthorized changes
- Monitor runtime behavior using endpoint protection or tamper-detection libraries
Automating Code-Integrity Checks Across the SDLC
Manual reviews alone can’t keep pace with modern release velocity. To maintain end-to-end software integrity, teams automate a chain of code integrity checks from commit to runtime:
- Commit: Git pre-commit hooks reject unsigned commits or code that bypasses linters.
- Merge/PR: Branch protection rules enforce two-person review and verify that the commit signature matches the author’s key.
- Build: CI jobs sign artifacts with Sigstore/Cosign and embed a provenance file. Any downstream job fails if the signature is missing or altered.
- Deploy: CD pipelines validate signatures again and compare the build hash to an allow-list defined in the code integrity policy (e.g., Kubernetes admission controller or WDAC policy file).
- Runtime: Host agents continuously hash binaries and scripts, alerting if anything deviates from the approved fingerprint.
Automating these gates turns integrity from a checklist into a safety net that fires 24/7, even when developers are asleep.
Tools that Help
A few tools and platforms to consider integrating:
- Jscrambler Code Integrity
- Zencoder Code Integrity Glossary
- Git hooks and pre-commit checks
- SAST (static application security testing) tools
- Microsoft WDAC for Windows-based environments
- Software bill of materials (SBOM) tools like CycloneDX
Final Thoughts
Code integrity isn’t just a backend concern; it’s every team member’s responsibility. With signed builds, secure pipelines, and clear policies, you turn “hope the code is clean” into “know the code is clean.” The result: safer software, happier users, and fewer late-night emergencies.