Modern organizations are facing significant challenges in resource management and allocation across departments. With 43% of HR leaders lacking a concrete future work strategy and 38% of employees reporting burnout due to ineffective processes and systems, strategic engineering allocation has never been more critical.
As engineering projects become increasingly complex, understanding and implementing an effective engineering resource allocation model in the software engineering industry has become crucial for organizational success.
What is engineering allocation?
Engineering allocation is the strategic planning and distribution of resources, people, budgets, materials, and time to complete engineering projects efficiently while meeting organizational goals. In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, this practice has transformed from simple task assignments to complex resource optimization and management systems designed to handle changing project requirements.
Core components of engineering allocation
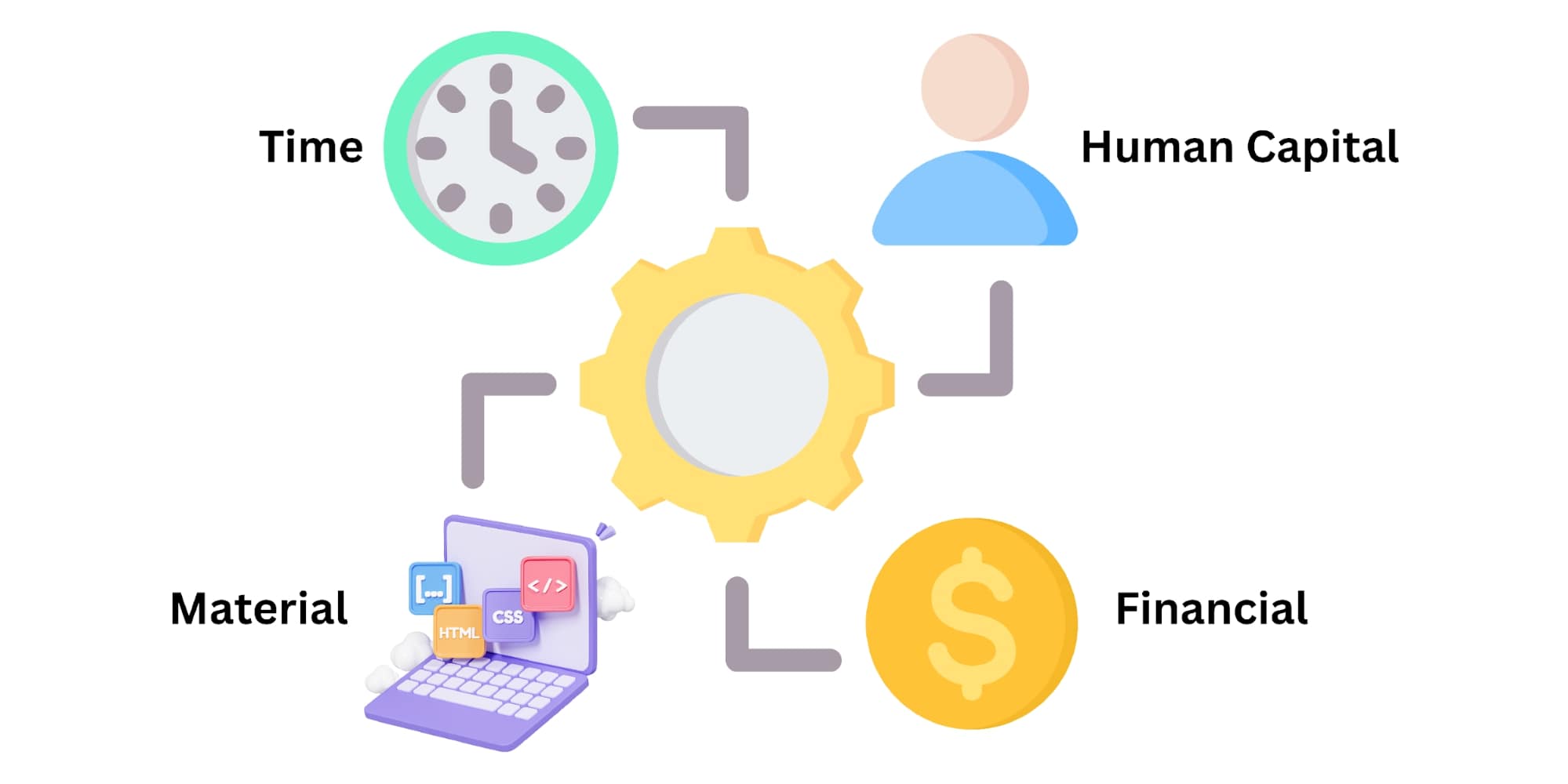
The foundation of resource allocation model in software engineering rests on four primary pillars:
- Human capital management: Make sure people with the right skills are assigned to the right tasks. This boosts efficiency and improves project delivery.
- Financial resource optimization: Allocate funds wisely to keep projects on track and avoid overspending. Companies with strong budgeting systems reduce cost overruns.
- Material resource coordination: Organize tools, equipment, and supplies effectively. Businesses that track materials carefully cut down on waste.
- Time management integration: Plan and monitor schedules to meet deadlines. Companies using time-tracking tools often stick to schedules better.
Benefits of effective engineering allocation
1. Improved productivity
- Engineers work on tasks that match their skills and expertise to enhance efficiency.
- Proper task distribution reduces idle time and bottlenecks, ensuring consistent output.
2. Cost efficiency
- Resources are allocated based on priority, minimizing waste and ensuring budgets are effectively utilized.
- Aligning resource usage with project goals and timelines helps businesses avoid unnecessary expenses.
3. Faster time-to-market
- Streamlined workflows and better task distribution accelerate project delivery, keeping businesses competitive.
4. Enhanced quality
- Engineers can focus on quality rather than multitasking, leading to more reliable and well-tested solutions.
- Proper workload management prevents burnout, ensuring sustained performance and attention to detail.
5. Better risk management
- Balanced workloads and clear ownership reduce project risks by avoiding resource overutilization or underutilization.
- Clear ownership and accountability improve visibility, making it easier to identify and address risks early.
How to optimize the engineering allocation process
1. Track team utilization
- Tracking team utilization rates and project performance metrics helps measure productivity and identify improvement areas.
- Metrics like sprint completion rates, code quality metrics, and delivery timelines can be used for this.
2. Compare metrics
- Analyze sprint velocities and delivery patterns across teams to understand performance trends.
- Compare planned versus actual delivery times and identify patterns that impact resource allocation effectiveness.
3. Acknowledge bottlenecks
- Identify resource bottlenecks and allocation inefficiencies by regularly assessing workflow delays, workload imbalances, and skill gaps that may impede project progress.
4. Capacity planning
- Assess current engineering bandwidth by evaluating team size, skills, and existing commitments.
- This will help to determine the available capacity for new projects and maintenance work.
5. Resource distribution
- Balance workload across engineering teams by evenly distributing tasks based on complexity, priority, and team capacity.
- This helps to prevent burnout and maintain productivity.
6. Allocation monitoring
- Track resource utilization in real-time using project management tools and dashboards.
- It ensures optimal resource usage and detects allocation issues early.
Challenges of engineering allocation
1. Global distribution
- If teams are distributed across the world, they will face coordination challenges in time zones, work styles, and local regulations.
- This requires flexible management systems that accommodate regional differences while maintaining project progress.
2. Technology integration
- Organizations must integrate legacy and modern systems while maintaining security and data integrity.
- For example, automotive companies need to connect traditional engineering systems with new software platforms and AI tools.
3. Cross-functional alignment
- Each project requires careful consideration of engineering capacity, skill distribution, and project priorities to ensure optimal resource utilization.
- Team leads must regularly assess and adjust allocations based on project demands and available expertise.
Future trends and innovations
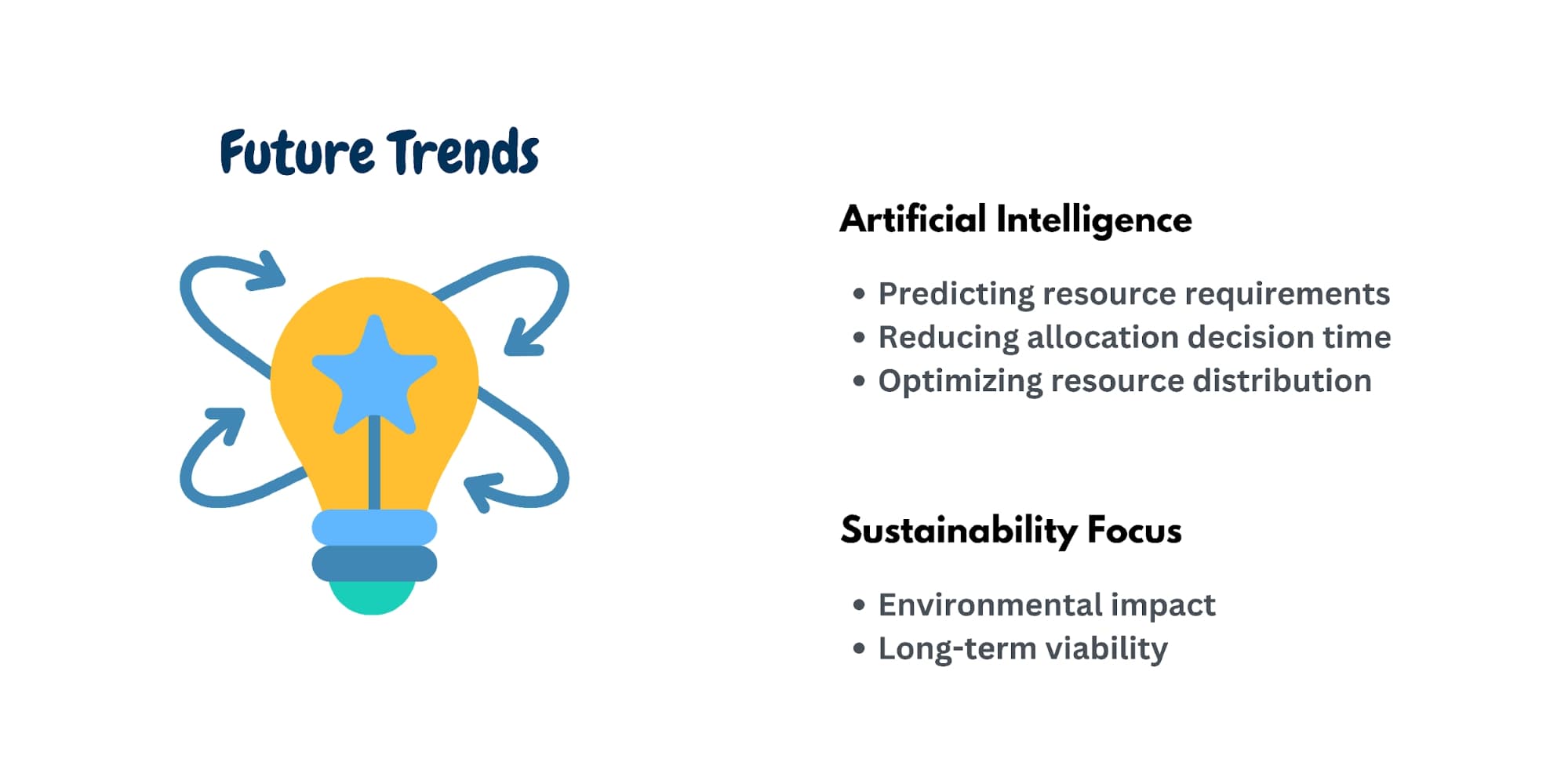
Artificial intelligence integration
AI-powered allocation tools are revolutionizing resource management by:
- Predicting resource requirements with higher accuracy.
- Reducing allocation decision time.
- Optimizing resource distribution through machine learning algorithms.
Sustainability focus
1. Sustainable development practices:
- Allocate dedicated time for technical debt management and system maintenance to ensure long-term codebase health.
- Include time for documentation and knowledge transfer activities in resource planning.
2. Long-term viability:
- Ensures sustained resource availability. For instance, engineering teams implement cloud-based resource-sharing reports to increase productivity in new projects while reducing physical infrastructure needs.
Best practices for implementation
1. Clear objective setting
- Set specific, measurable goals at all organizational levels.
- Each objective should have defined success metrics and clear ownership to track progress effectively.
2. Resource assessment
- Evaluate current engineering capabilities and talent against project needs.
- Identify skill gaps and areas of strength to optimize resource allocation and determine training or hiring requirements.
3. Performance monitoring
- Track key metrics and milestones without micromanaging.
- Use straightforward dashboards and regular check-ins to maintain visibility while keeping teams productive.
4. Process improvement
- Regularly review and update workflows based on team feedback and project outcomes.
- Enable teams to suggest and implement process changes that increase efficiency.
Wrapping Up
Engineering resource allocation continues to evolve as a critical component of project success. Organizations that adapt to emerging trends while maintaining fundamental principles position themselves for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Future success in engineering allocation will depend on organizations’ ability to balance traditional methodologies with innovative approaches, ensuring optimal resource utilization while maintaining project quality and stakeholder satisfaction.