Building software isn’t just about going fast – it’s about getting the right balance.
Often, teams prioritize speed and throughput. But speed without balance slows you down. When you focus solely on throughput, hidden bottlenecks, bugs, and security issues start to pile up. Flow Distribution is one of the core flow framework metrics that fixes this blind spot. It tracks how much of your effort goes to features, defects, risk work, and debt, so you can spot imbalances early and steer the team before quality or delivery slips.
What is Flow Distribution?
Flow distribution tracks how your team’s work is divided across different types of work. It shows exactly where your time and effort go.
Typical categories:
- Features: New functionality and capabilities that add value.
- Defects: Bug fixes and issues that need solving.
- Risks: Security patches and compliance work that are crucial for staying safe.
- Debt: Technical debt cleanup and system improvements.

Why Flow Distribution Matters
Understanding your flow distribution prevents common team pitfalls and creates sustainable delivery.
Avoiding imbalance:
- Too much feature work can lead to rising tech debt and system instability.
- Too much bug fixing means innovation slows and competitors pull ahead.
- Ignoring risks leads to security issues and compliance problems later.
Value of monitoring:
- Keeps the right mix of work for long-term success.
- Improves predictability by showing realistic team capacity.
- Boosts stakeholder alignment through clear visibility into work allocation.
- Reduces team stress by avoiding last-minute emergencies and reactive workflows.
Understanding Flow Distribution in Context
Flow distribution provides unique insights that complement your existing delivery metrics.
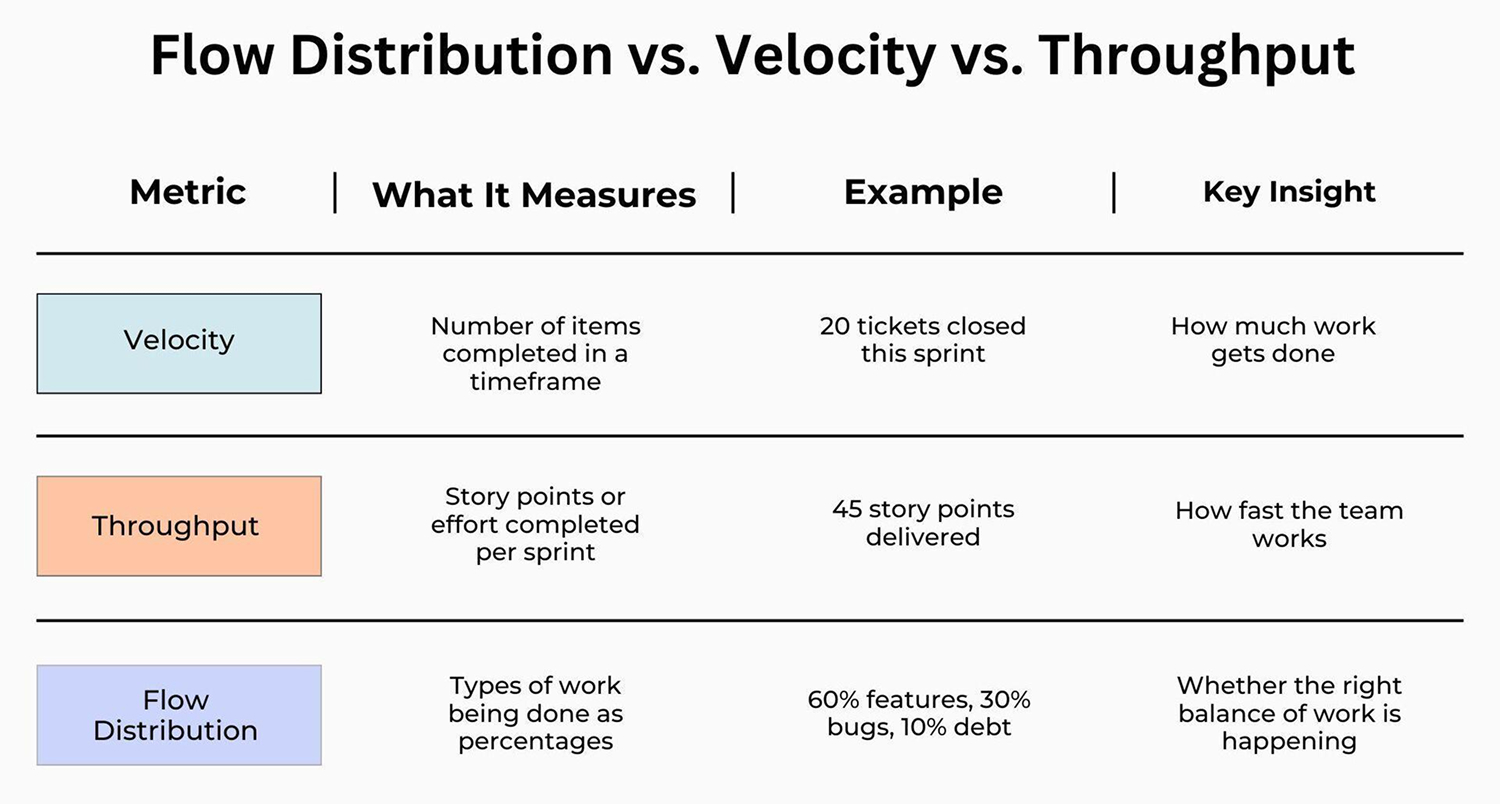
Flow Distribution vs. Velocity:
- Velocity measures how fast developers deliver story points or code.
- Flow distribution shows how the work is balanced across features, defects, risk, and debt.
- Flow distribution protects teams from chasing speed at the expense of quality.
Flow Distribution vs. Throughput:
- Throughput measures the number of items a team completes within a specified timeframe.
- Flow distribution adds context: what kinds of items are those?
- High throughput focused only on bugs may hide mounting debt elsewhere.
How to Measure Flow Distribution
Measuring flow distribution works best when integrated with existing flow and delivery metrics.
Tools and methods:
- Kanban boards with proper work item categorization and labels.
- Jira categories and issue types for automatic tracking.
- Value stream management tools for comprehensive flow analysis.
- Simple spreadsheets for basic percentage calculations.
Metrics to track:
- Number of items in each category per week or sprint.
- Percentage split across categories over time.
- DORA flow metrics (deployment frequency, lead time, recovery time, change failure rate) segmented by distribution.
- Time spent in each category compared to the planned allocation.
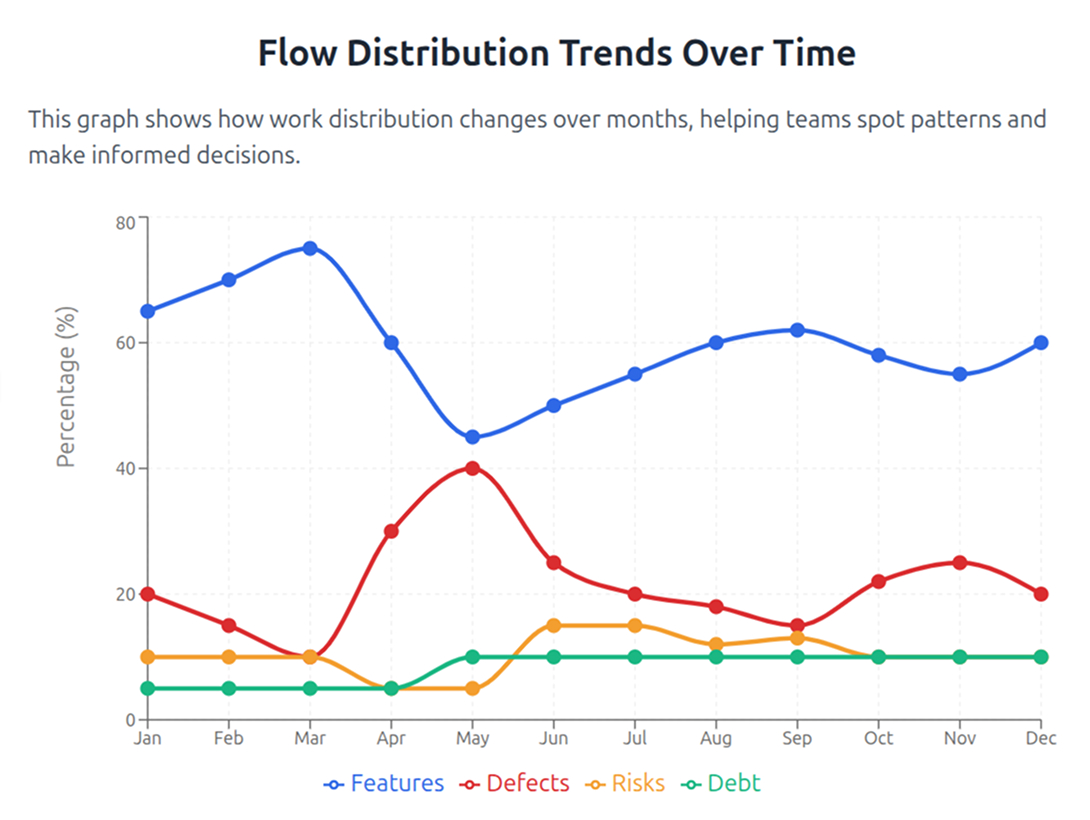
Interpreting Flow Distribution Trends
Your flow distribution patterns tell a story about your team’s health and priorities.
Example scenarios:
- A spike in defects signals quality issues in recent releases or processes.
- A growing tech debt percentage means you need dedicated refactoring time.
- Low-risk-related work reveals potential compliance blind spots or security gaps.
- Sudden feature drops often indicate firefighting mode or resource constraints.
Strategies for Balancing Flow
Once you understand your patterns, you can actively manage your work distribution.
Key strategies:
- Set WIP (work in progress) limits per type to prevent overloading any category.
- Regularly review distribution in retrospectives to catch imbalances early.
- Use objectives and key results (OKRs) or team goals to guide distribution targets and priorities.
- Reserve capacity for each work type based on historical data and business needs.
- Create explicit policies for when to shift focus between categories.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Teams often make these mistakes when managing flow distribution.

- Overloading a feature with work without room for bugs or debt creates technical instability.
- Treating flow distribution as static instead of dynamic, missing seasonal or project changes.
- Ignoring risk and compliance until it’s too late, leading to emergency fixes.
- Micromanaging percentages instead of focusing on sustainable team capacity.
- Abandoning distribution goals during crunch periods when they matter most.
Wrapping Up
Flow distribution tracks where your effort goes, whether into features, bug fixes, risk work, or technical debt cleanup. High-performing teams always watch those patterns. A sudden spike in bug tickets or an ever-shrinking slice of debt work is a red flag that they should address early.
The most successful organizations deliver at a sustainable pace because they balance new value with quality and stability. Flow distribution helps you answer one simple question: Are we shipping smart, or just shipping fast?