How Automated Code Reviews Reduce Costs and Improve ROI
Status
answered
Status
answered
Today, software development teams are shipping products like never before. However, without an appropriate structure in place, speed becomes an open invitation to disorder. As the codebase grows, the project’s deadline approaches, and the manual review process has reached a bottleneck. Reviewers are drowning in the backlog, and queued pull requests go unprocessed to the point where production becomes riddled with bugs.
Automated code reviews are the easiest solution to this challenge.
These tools check all commits for code style issues, logic problems, potential security risks, and a whole lot more, all within the CI/CD pipeline and in real-time. They improve quality, minimize mistakes, and most importantly, help teams streamline time and resources.
In this article, we’ll explore how automated code reviews help modern teams, best practices, real challenges, and key metrics that matter.
Automated review replaces routine human checks with repeatable machine rules. These checks range from simple things like:
To more advanced concerns, such as:
Automated systems, unlike manual systems, do not get tired, forget to do one of the checks, or skip a review. These systems adhere to rules during any hour of the day and regardless of how intricate the change is, making no exceptions.
| Aspect | Manual Review | Automated Review |
| Speed | Hours to days | Seconds to minutes |
| Consistency | Varies by reviewer | Uniform |
| Focus | Style, Logic | Style, Security, Best Practices |
| Scalability | Limited to team capacity | Easily scales with code volume |
| Cost | High (human Hours) | Low (Once set up) |
Properly implemented automated code review systems do not substitute a developer’s evaluation; rather, they enhance it. The developer’s tasks become easier and less tedious, allowing them to center on the architecture, logic, and user experience of the application.
Let’s look at where the savings really happen.
Traditionally, developers wait hours (or even days) to get comments on a pull request. By then, context is lost, and they might have already moved on to another task.
With automation:
A report from Codacy found teams using automated review tools cut review cycles by 60% or more.
Think about it: if your team completes 30 PRs/week and saves 15 minutes per PR, that’s 7.5 hours reclaimed, every single week.
According to IBM, fixing a bug after release can cost 15 to 100 times more than catching it during development.
Automated reviews help catch run-time errors like:
By eliminating trivial bugs at commit time, teams drastically reduce the volume of regressions and production incidents, saving both developer hours and reputation damage.
Every developer has their style. Some prefer snake_case, others like camelCase. Some add comments. Others don’t. Over time, this turns your repo into a minefield of mixed conventions and misunderstood logic.
Automated tools solve this by enforcing coding standards across the board:
Senior engineers are expensive. They should be solving complex problems, not flagging missing semicolons.
With automation:
That leaves human reviewers to focus on:
This shift is essential in fast-paced environments, where every hour saved compounds over time.
To measure ROI from code review automation, a simple formula is:
ROI = (Hours Saved × Hourly Rate) – Tooling Cost
Example:
Savings per week:
10 devs × 5 PRs × 0.25 hrs × $50 = $625/week
Monthly: $2,500
Annually: $30,000
That’s before you even count the reduction in bugs, downtime, or onboarding time.
| Metric | Manual | Automated |
| Average PR Turnaround | 8 hours | 1 hours |
| Bugs per 1000 Lines | 4.2 | 1.8 |
| Cost of Missed Bugs | $12,000/quarter | ~$3,500/quarter |
The ROI is clear. And with most tools offering open-source or low-tier free plans, the entry barrier is lower than ever.
Automation works best when it’s tailored. Here’s how to get the most from it:
No two codebases are the same. Avoid default rules that create noise.
Tip: Use tools like Codacy or SonarCloud to configure rule profiles per repo.
Waiting until merge time to review is too late.
Instead:
This ensures quality isn’t an afterthought; it’s enforced from the start.
# Example GitHub Actions snippet
name: Code Quality
on: [push]
jobs:
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Run ESLint
run: npm run lintDon’t ditch human reviewers entirely.
Use automation for:
Use humans for:
This division boosts coverage while reducing burnout.
If developers start getting too many alerts, they will start ignoring them. So, make sure to:
Numbers show whether your rules help or hurt. Start with four easy ones:
These KPIs indicate whether your system is helping or just creating noise.
Automation isn’t a silver bullet. While the benefits are significant, there are a few challenges you need to be aware of.
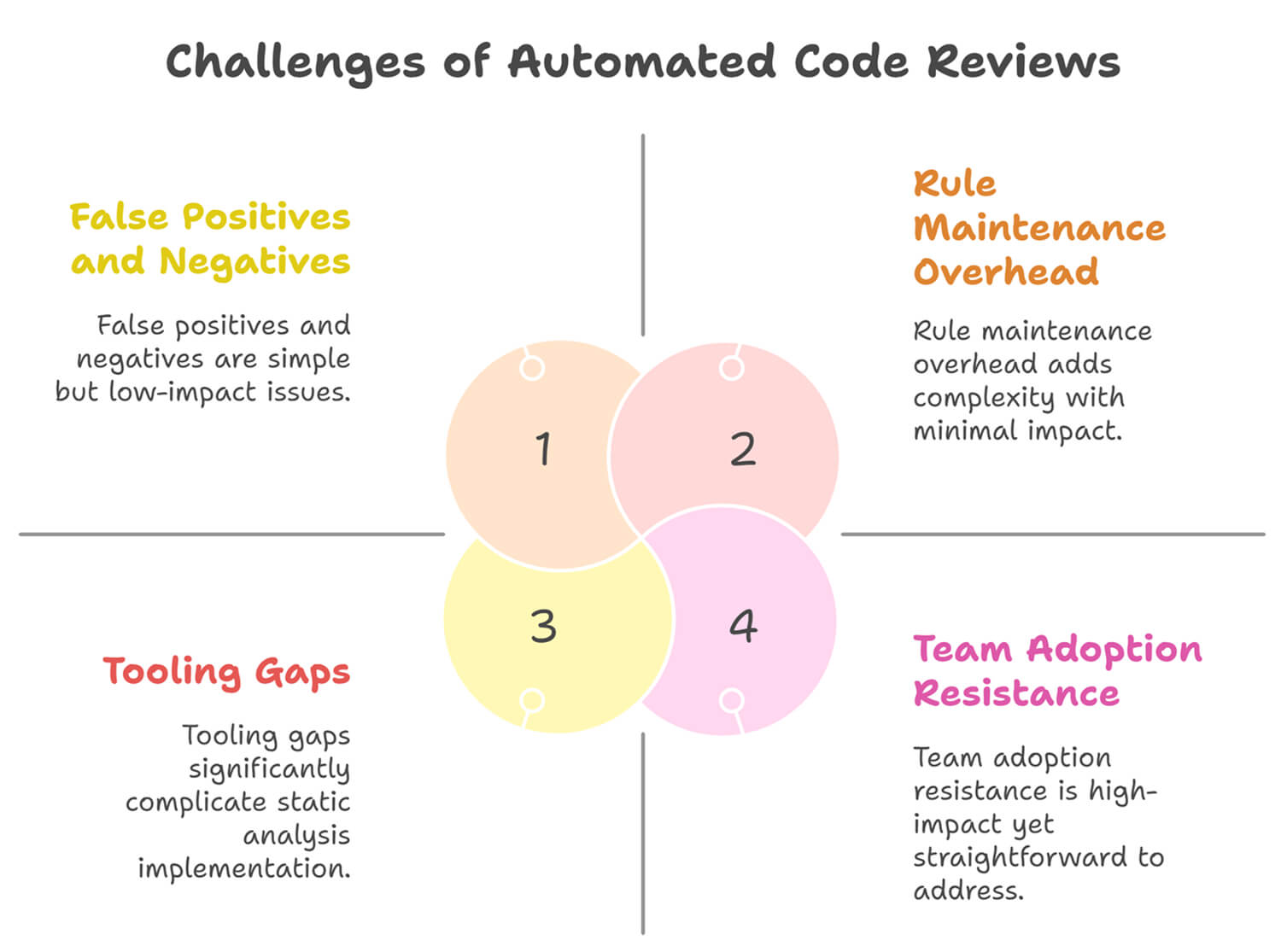
These errors frustrate developers and undermine adoption.
What to do:
Your codebase evolves. So should your rules. That means:
Without this, your automation becomes stale, and developers start ignoring it.
Tip: Assign rule ownership to a tech lead or create a monthly code quality audit.
Automated scanners are powerful, but they only work on patterns they understand. Anything that requires domain knowledge or broader context still needs a human eye:
A hybrid approach is key:
Even the smartest tool fails if developers don’t use it. Common objections:
To fix this:
When developers see that automation helps them ship faster and safer, the tool becomes an ally rather than an obstacle.
Reviewing code the traditional way is simply too slow and ineffective for today’s software companies. With the right practices and tools, automated code reviews can:
But like any good system, success hinges on smart adoption. Customize your rules. Blend automation with human oversight. Track what works and improve what doesn’t.
Implementing the right strategy will make automated code review a fundamental component of your engineering strategy.