What are the Pillars of Engineering Management Excellence?
Status
answered
Status
answered
You probably have been in the position where you have sat in front of a computer, trying to prioritize tickets. The constant context-switching and the unclear requirements can easily demotivate developers. However, you don’t need to worry about such things if your team has a solid engineering management process.
Effective engineering management rests on six key pillars. These principles of operational effectiveness can help an organization build a sustainable environment with high productivity and improvement. In addition, these principles can transform underperforming teams into high-performing ones. Engineering leaders can use these principles to foster creativity and sustainability in everyday operations.
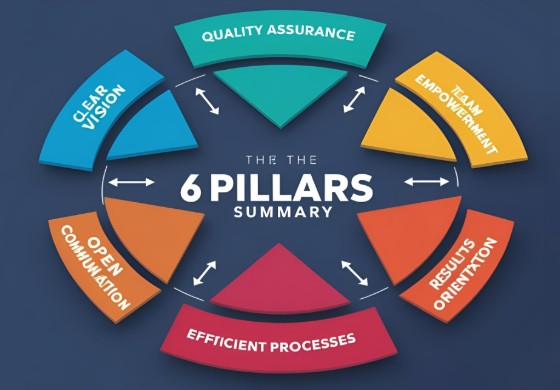
A well-defined vision aligns engineering efforts with business objectives. Engineers need more than just tasks-they need context. Understanding the ‘why’ behind technical decisions fosters engagement and purpose.
Key Principles:
Quality should not be an afterthought. It should be embedded in the development process. Weak security foundations lead to fragile systems, resulting in production failures and unnecessary firefighting.
Key Principles:
Empowered teams perform at their best when they feel ownership and responsibility for their work. Encouraging diverse voices and fostering psychological safety will lead to innovation and growth.
Key Principles:
Effective engineering teams don’t work in isolation. They are always in sync with stakeholders. Misalignment between teams can lead to inefficiencies, missed deadlines, and unclear expectations.
Key Learnings:
Engineering teams often struggle with inefficiencies like redundant meetings, approval bottlenecks, and manual repetitive tasks. Streamlining workflows improves productivity and allows engineers to focus on meaningful work.
Key Learnings:
The ultimate goal of engineering efforts is to create tangible value for users and the business. Tracking meaningful outcomes rather than just outputs ensures that engineering contributes effectively to team success.
Key Learnings:
Engineering management is more than just supervision of code and systems. It’s about enabling talented individuals to contribute in a positive way. Vision, quality, empowerment, communication, efficiency, and results are the six principles of operational excellence that guide successful engineering teams.
Excellence in engineering is an ongoing journey. By continuously reinforcing these principles, teams can build resilient, innovative, high-performing teams that drive long-term success. A culture of learning, adaptation, and collaboration will ensure engineering teams remain effective in the face of evolving industry demands.