Software today is nothing like it was ten years ago. Even a tiny backend service can depend on hundreds of open-source packages, each with its own version, extra packages, license, and hidden risks. Engineering leaders must move fast while keeping this “software supply chain” safe from attack.
That’s where software composition analysis (SCA) helps. Once a nice extra, SCA is now essential. Whether you run a small startup or several large teams, you need clear visibility, automated scans, and data-driven ways to reduce risk.
Guides from tools such as SonarSource and Cycode show how quickly SCA has matured and why teams rely on it to protect their dependencies.
In this article, we’ll explain SCA in plain language, show why it matters, list five key benefits for engineering leaders, and answer common questions with simple diagrams and tables.
What Is Software Composition Analysis (SCA)?
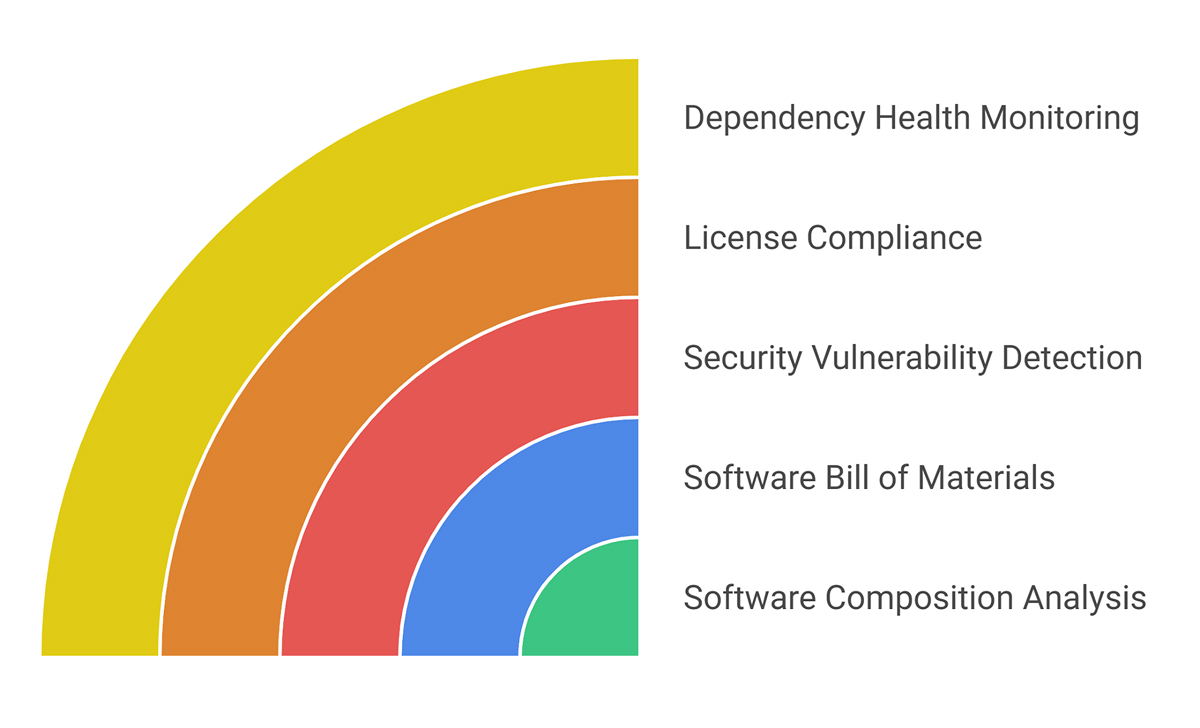
At its core, software composition analysis (SCA) is the practice of scanning, identifying, and managing all open-source components inside your application. It relies heavily on generating a software bill of materials (SBOM), which is an inventory of all external libraries, modules, and dependencies.
Engineering teams use SCA tools to:
- Find security holes
- Keep an eye on old libraries
- Get to know transitive dependencies
- Find out what your license obligations are
- Keep an eye on the health of your dependencies over time.
Think of SCA as a “dependency MRI scan”. It clearly, consistently, and automatically shows you what’s inside your software. SCAs offer many benefits; here are the top 5:
Benefit 1: Stronger Security Through Vulnerability Detection
Most modern applications depend on hundreds of open-source libraries. Any one of those can introduce a critical vulnerability, sometimes deep in a transitive dependency that no one on the team has ever heard of.
SCA tools continuously scan these components and compare them against vulnerability databases (such as NVD or vendor advisories). For every library and version, they check:
- Are there known CVEs for this version?
- How severe are they?
- Are there known exploits?
- Is there a safer version available?
Instead of relying on someone in the team to “notice a security blog post,” you get a structured, automated view of risk across all your services. High-severity issues can manifest as tickets, pipeline failures, or alerts, and teams can quickly identify which service and dependency needs attention.
Over time, this changes the organization’s posture. You’re no longer merely reacting to incidents; you’re continuously reducing exposure before code ever reaches production.
Benefit 2: Improved Visibility with a Complete Bill of Materials
Without SCA, many leaders can’t answer a simple question: “What third-party components are we actually shipping?” That’s risky in itself.
SCA solves this with a complete software bill of materials (SBOM), a machine-readable inventory of every external component your applications rely on. An SBOM records the following for each element:
- Name and version
- Direct vs. transitive dependency
- License type
- Known vulnerabilities and status
- Source (registry, repository, origin)
This SBOM is now the main source of information for security, engineering, and compliance. You don’t have to guess if you’re affected when a new CVE is announced. You can just look up the SBOM and see right away where that library is used in microservices, images, or environments.
Visibility also makes it easier to make technical decisions every day. Teams can find groups of legacy packages and services with overly complex dependency trees, and plan upgrades or refactorings based on real data rather than guesswork.
Benefit 3: Faster and More Reliable CI/CD with Automated SCA Scans
Running SCA manually from time to time creates friction. It works much better when integrated directly with your CI/CD pipelines.
In a standard configuration, every pull request or build in the main branch triggers the SCA step by default. It consists of the following:
- Creating or updating the SBOM
- Identifying vulnerabilities and license terms
- Providing a clear pass/fail result with thorough analysis
From a developer’s perspective, it feels similar to linting or unit tests. If there’s a critical security issue or an unacceptable license issue in the dependency, the build pipeline will fail with clear instructions about what happened and how to fix it.
For engineering executives, there are three key takeaways:
- Consistency: Each repo and service receives the same check.
- Speed: Problems can be identified early when changes are small and can be easily resolved.
- Confidence: A green pipeline indicates that both functional and license checks succeed.
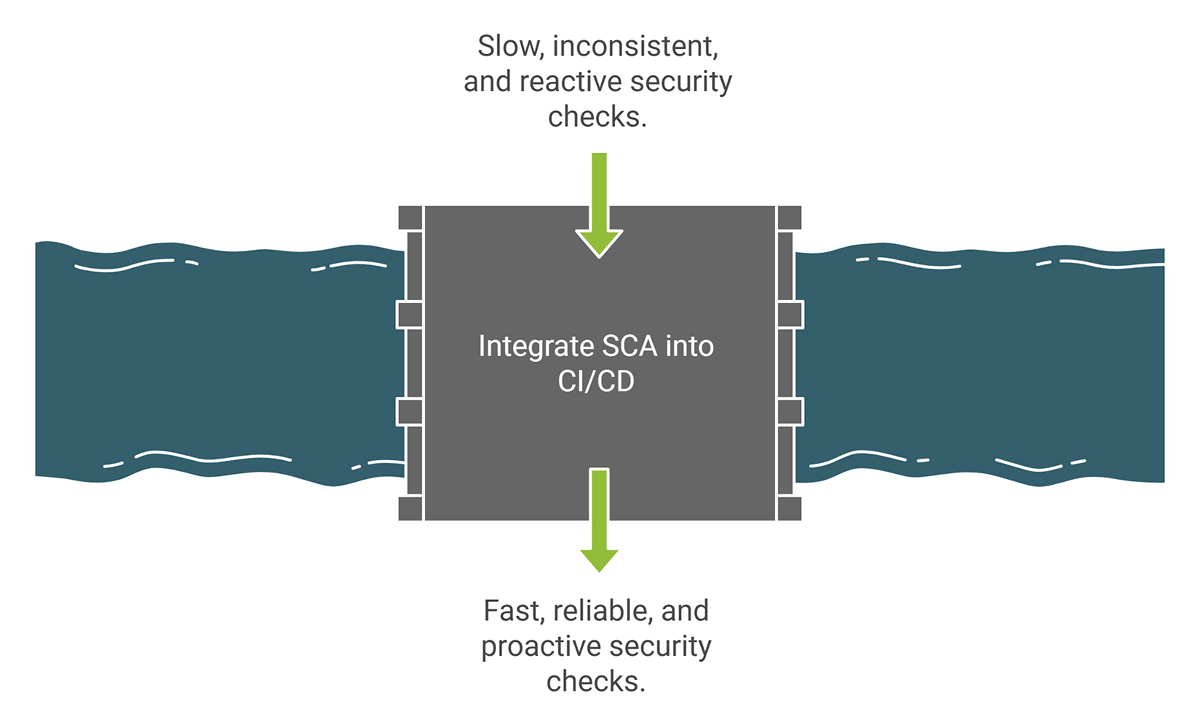
As a result, releases can be forecasted. Rather than having surprises during security reviews, risk mitigation happens in regular development.
Benefit 4: Reduced Legal and Licensing Risks
Open-source licensing can present problems if you’re not aware of your licensing obligations from the outset. Depending on the licensing conditions, you may be locked into additional obligations, such as disclosing your code, publishing code updates/general modifications, or including specific notices.
With that in mind, SCA tools help manage the above problems by:
- Identifying the license associated with each dependency
- Identifying and warning users of components that have restrictive/incompatible licensing
- Identifying and warning users of license ambiguity/non-disclosure
- Implementing your organizational policies, such as no AGPL in production
Imagine if, for instance, a team accidentally introduced a GPL-licensed component into a proprietary product. Instead of allowing that component to go into production and causing headaches during an audit or due diligence, SCA can identify it early and recommend alternatives to the team.
This helps reduce your organization’s legal risk and makes it easier to collaborate with legal and compliance experts on licensing matters. The SCA process helps ensure that using open-source components in your organization adheres to your organization’s legal compliance policies while also addressing your customers’ needs.
Benefit 5: Data-Driven Engineering Decisions Through SCA Metrics
SCA is not just a scanner; it’s also a source of valuable operational data about how your teams manage dependencies and risk.
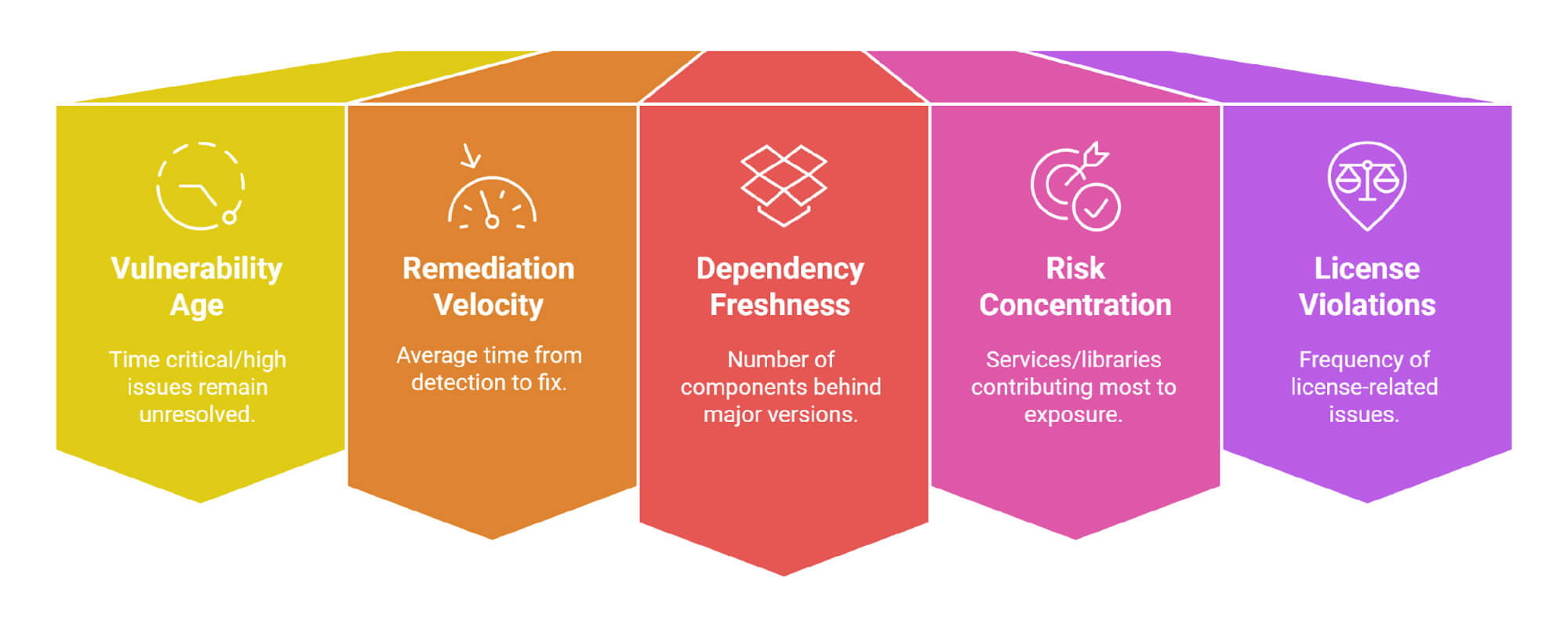
Most mature SCA platforms expose metrics such as:
- Vulnerability age: How long critical/high issues remain unresolved.
- Remediation velocity: Average time from detection to fix.
- Dependency freshness: How many components are behind by one, two, or more major versions?
- Risk concentration: Which services or libraries contribute the most to your overall exposure?
- License policy violations: How often do teams bump into license-related issues?
These metrics help leaders move from gut feeling to measurable improvement. You can:
- Set targets (e.g., “no critical vulnerabilities older than 7 days”)
- Identify teams or services that need support with dependency hygiene
- Justify investment in modernization or refactoring work
- Track progress quarter over quarter
Instead of treating SCA as a one-off security tool, you turn it into a continuous feedback loop that shapes priorities, staffing, and technical strategy.
FAQ
1. How does SCA improve software security for development teams?
SCA improves security by automated detection of weaknesses in both direct and transitive dependencies. It guarantees that insecure or unmaintained libraries never hit production. When coupled with automated pipeline policy enforcement, it automatically and significantly shrinks the attack surface for supply chain theft.
2. What’s the difference between SCA and traditional vulnerability scanning?
Traditional scanners focus on your application code and runtime environment. SCA is concerned with your open-source components. While vulnerability scanners look for misconfigurations or coding mistakes, SCA searches for risks hidden in third-party libraries. They are both needed as they protect different layers.
3. What metrics should team leaders track when using SCA tools?
Proposed metrics include:
- Age of vulnerabilities
- Speed of remediation
- Freshness of dependencies
- Quantity of high-risk libraries
- License conflicts
These metrics illuminate the level of engineering discipline, code hygiene, and the amount of chronic tech debt.
4. How can SCA be integrated into CI/CD pipelines effectively?
Integrate SCA as early in the pipeline as is practical, ideally at the PR stage. Set severity thresholds, enable automatic pass/fail, and direct send feedback to the developers. Rareness and documentation are a must for exceptions. Once the groundwork is settled, SCA enforcement becomes frictionless.
5. What are the top challenges engineering leaders face when implementing SCA?
Some familiar challenges include:
- Resistance to defect building
- Insignificant disruptions
- No one’s responsibility
- Regulating transitive dependencies
- Augmenting SCA with current tools
The usual answer revolves around rules, automation, and communication.
Conclusion
Software composition analysis is no longer an advanced or optional security practice; it’s part of the foundation on which modern engineering relies. Open-source ecosystems move fast. Vulnerabilities surface overnight. License requirements change. Dependencies shift under your feet.
SCA provides engineering leaders with data and the capability to adapt to change.
To recap, SCA empowers teams through:
- Improved vulnerability detection
- Full visibility through SBOMs
- Accelerated and secure CI/CD pipelines
- Reduced legal and licensing risk
- Data-driven engineering knowledge
In many sectors, SCA has emerged as an important element of the secure development lifecycle. The ever-increasing number of attacks in the software supply chain makes SCA one of the most useful tools at the disposal of current leaders. By starting early, automating effectively, and using metrics optimally, your organization establishes secure, scalable engineering in both the current and future eras.