What is the formula used to calculate flow efficiency?
Status
answered
Status
answered
Flow efficiency is an important metric in the software development life cycle. It helps organizations understand how efficiently they work by measuring the actively spent time versus the total time taken to complete a task. This article will cover what flow efficiency is, the factors affecting it, and how to calculate and improve it.
Flow efficiency measures how effectively work is completed in a project. In software projects, work can be delayed due to dependencies, approvals, resource availability, or other constraints. Flow efficiency calculates the time spent on value-adding activities out of the overall task completion time.
Flow efficiency is an important aspect of Agile methodologies, lean development, and service delivery models, where the main goal is to optimize productivity. It helps teams and organizations shift their focus from merely completing tasks to enhancing overall process performance.
The formula to calculate flow efficiency is described below.
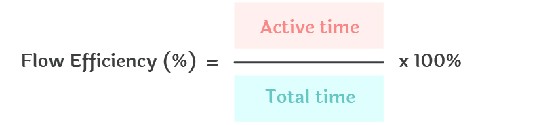
Flow efficiency is the ratio of the total active, productive time to the total time of the process, expressed as a percentage
For example, consider a software development team that took 10 days to complete a task. Out of these 10 days, only four were spent on software development. Six days were spent on getting approvals, resolving dependencies, and other delays. This means that only 40% of the total cycle time was used for productive work, while 60% was lost to delays.
Several factors can impact flow efficiency.
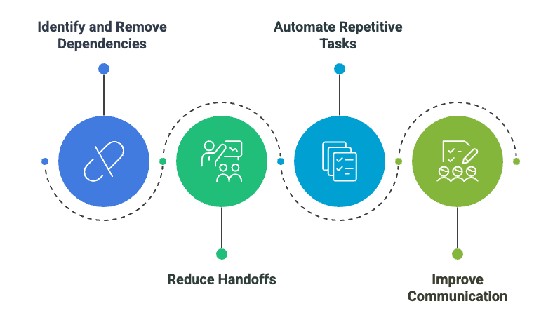
Organizations can follow these best practices to eliminate the factors mentioned above and improve flow efficiency.
Flow efficiency is widely used throughout many industries.
Flow efficiency is an important metric for identifying process effectiveness. It can be calculated by measuring the active work time compared to the total time spent on a task. Multiple factors affect flow efficiency, including dependencies, handoffs, and lack of automation.
Flow efficiency can be increased by providing solutions to these issues and following best practices. Improving flow efficiency not only improves team performance but also leads to better customer satisfaction.